Different Components in Powerpoint
Talking about PowerPoint Presentations, they are one of the media through which many businesses work in order to explain the project related stuff or presenting the seminar on your paper or subject.
PowerPoint is the product of Microsoft which is included in a Microsoft Office Suite that also includes Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, Access, Outlook, OneNote and many more.
PowerPoint became a component of the Microsoft Office Suite, first offered in 1989 for Macintosh and in 1990 for Windows, which bundled several Microsoft apps. Beginning with PowerPoint 4.0 (1994), PowerPointwas integrated into Microsft Office development and adopted shared common components and a converged user interface.
PowerPoint's market share was very small at first, prior to introducing a version for Microsoft Windows, but grew rapidly with the growth of Windows and of Office. Since the late 1990s, PowerPoint worldwide market share of presentation software has been estimated at 95 percent.
PowerPoint was originally designed to provide visuals for group presentations within business organizations but has come to be very widely used in many other communication situations, both in business and beyond. The impact of this much wider use of PowerPoint has been experienced as a powerful change throughout society, with strong reactions including advice that it should be used less, should be used differently, or should be used better.
The first PowerPoint version (Macintosh 1987) was used to produce overhead transparencies, the second (Macintosh 1988, Windows 1990) could also produce color 35mm slides. The third version (Windows and Macintosh 1992) introduced video output of virtual slideshows to digital projectors, which would over time completely replace physical transparencies and slides. A dozen major versions since then have added many additional features and modes of operation and have made PowerPoint available beyond Apple Macintosh and Microsoft Windows, adding versions for IOS, Android, and web access.
Following the overall GUI of PowerPoint-
Above given is the image of the screen of PowerPoint, which includes many components present in theirs. Here we have presented a Presentation in the Image, which will explain to you about the PowerPoint, if you need it, then comment on this post for the same.
Following are the components of PowerPoint:
- Quick Access: This button position top left portion, this toolbar is customizable, you can move this in two possible locations. This toolbar consists of a set of commands that is independent on the tab of the ribbon that currently displayed and you can add commands in this button.
- Title Bar: Position at the top of the user interface, where the file name will see hereafter saving a file, as a default once you open your MS-Office 2010 you will see it as Presentation 1-Microsoft PowerPoint.
- Control Tool Box: Located right top of the user interface, where you can close, restore and maximize, and minimize the windows program.
- Tab Menu: Tab Menu or tab of the ribbon-Position below of the title bar, this related to the type of activity, such as to relate a ribbon menu name, like once you click the home it will open as home ribbon menu. The tab menus are FILE, HOME, INSERT, DESIGN, TRANSITIONS, ANIMATIONS, SLIDE SHOW, REVIEW, and VIEW.
- Ribbon Menu: Position under the tab menus, if you need to see it or control it, hold CTRL key and press F1. This menu contains all the commands and other menu items that you can help to find the command easily to finish your work.
- Slide Sorter: Position left side of your user interface, all the slides will arrange in vertical order from the top as first slides down to your last slides. You can drag to rearrange the slides, delete, and other commands once you right click your mouse.
- Slide Template: This part is position at the center of your user interface, this is the biggest part where you can start and put your design in Presentation, animation, effects and more.
- Animation Pane: It is a part and command of ANIMATION PANE, once you click this button, it will open in the right side portion of the user interface. This pane or panel will display the animation functions you use in your slide template. Also, you can rearrange the animation and effects according to your own design.
- Zoom In and Out Slider Bar: This part position right side down and above of the taskbar. This is used to enlarge and decrease the view of your slide template at the center.
More:
- Add Notes and Note Pane: This pane or panel position at the bottom of your user interface. Which you can type notes that you can accompany a slide. You can print these notes as notes pages or display it when you save a presentation as a web page.
- Status Bar: This part position below of the user interface and left side of the zoom in/out sliding bar and view buttons of the slide show. This is only to notify what slide number you use in your application.
What's on the ribbon tabs?
The ribbon tabs group tools and features together based on their purpose. For example, to make your slides look better, look for options on the Design Tab. The tools that you use to animate things on your slide would be on the Animations tab.
Here's a look at what you'll find in each of the PowerPoint ribbon tabs.
1. Home

The Home tab holds the Cut and Paste features, Font and Paragraph options, and what you need to add and organize slides.
2. Insert
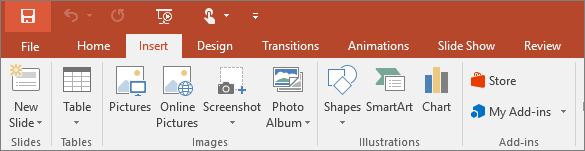
Click Insert to add something to a slide. This includes pictures, shapes, charts, links, text boxes, video and more.
3. Design
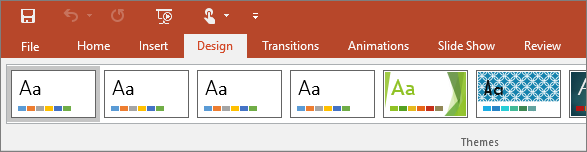
On the Design tab, you can add a theme or color scheme, or format the slide background.
4. Transition
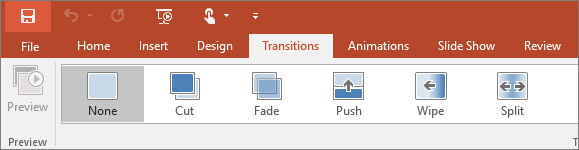
Set up how your slides change from one to the next on the Transitions tab. Find a gallery of the possible transitions in the Transition to This Slide group - click More
 at the side of the gallery to see all of them
at the side of the gallery to see all of them5. Animations
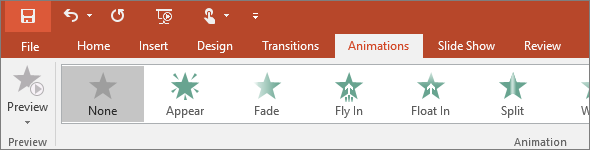
Use the Animations tab to choreograph the movement of things on your slides. Note that you can see many possible animations in the gallery in the Animation group, and see more of them by clicking More
 .
.6. Slide Show
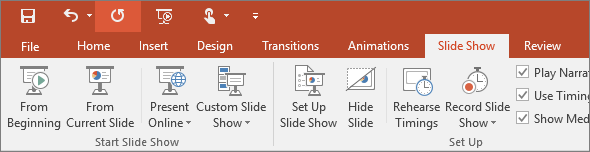
On the Slide Show tab, set up the way that you want to show your presentation to others.
7. Review
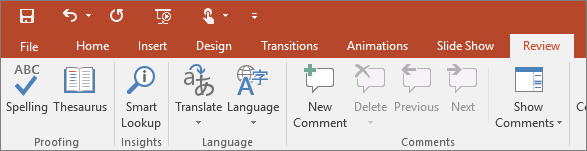
The Review tab lets you add comments, run spell-check, or compare one presentation with another (such as an earlier version).
8. View
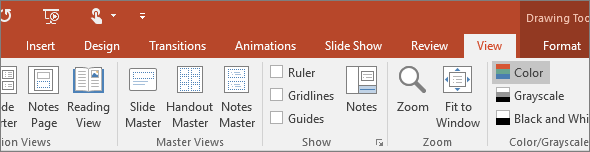
Views allow you to look at your presentation in different ways, depending on where you are in the creation or delivery process.
9. File
At one end of the ribbon is the File Tav, which you use for the behind-the-scenes stuff you do with a file, such as opening, saving, sharing, exporting, printing and managing your presentation. Click the File tab to open a new view called the Backstage.
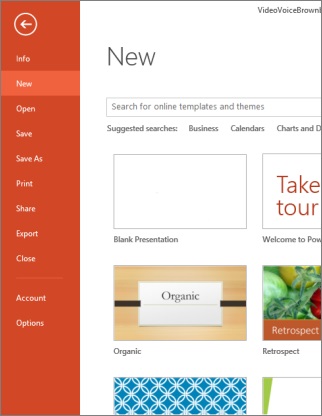
Click from the list on the side to do what you want to do; for example, click Print to find the options and settings for printing your presentation. Click Back
 to return to the presentation that you were working on.
to return to the presentation that you were working on.10. Tools Tabs
When you click some parts of your slide, such as pictures, shapes, SmartArt or text boxes, you might see a colorful new tab appear.

In this example above, the Drawing Tools tab appears when you click a shape or text box. When you click a picture, the Picture Tools tab appears. Other such tabs include SmartArt Tools, Chart Tools, Table Tools, and Video Tools. These tabs disappear or change when you click something else in your presentation.
If you want the detailed Blog about the sub Components of the Ribbon Tabs, then comment about the same in the same blog.




0 Comments